Method study is basically conducted to simplify the
work or working methods and must go towards higher productivity. It is always
desirable to perform the vital function with desired goal minimum consumption
of resources. Method signifies how a work is to be done, i.e. description of
how we consume resources in order to achieve our target?
Procedures of Method Study:
Select:
Work Selected for methodical study may be an identified problem area or
an identified opportunity. It may be identified through a systematic review of
obtainable data, normal monitoring or control processes. High levels of
dissatisfaction and complaint or as part of a change in management policy,
technology or location, and usually because it meets certain conditions or
urgency and/or priority.
Recording:
The Record stage of method study involves gathering sufficient data to
act as the basis of evaluation and examination.
Different types of Recording
Techniques:
Indicating Process Sequence:
1.
Outline Process Chart
2.
Flow Process Chart. Man Type, Material Type, Equipment Type.
3.
Two Handed Process Chart.
Using Time Scale:
1. Multiple Activity Chart,
Using Time Scale.
2. Simo Chart, Using Time
Scale.
3. P.M.T.S Chart
Diagrams Indicating
Movements:
1.
Flow Diagrams.
2.
String Diagram.
3.
Cycle graph.
4.
Chrono-cycle graph.
5.
Travel Chart.
Chart:
Symbols Used in Charts:
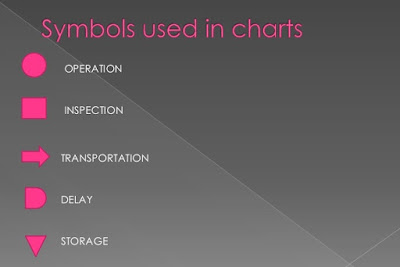
Operation: Indicates
the main steps in a process, method or procedure. Usually the part, material or
product concerned is modified or change during the operation.
Inspection: Indicates
an inspection for quality and/or check for quantity.
Transport: Indicated
the movement of workers, materials or equipment from place to place.
Temporary Storage Or Delay: Indicates
a delay in the sequence of events: for example, work waiting between
consecutive operation or any object aside temporarily without the record until
required
Permanent Storage: Indicates
a controlled storage in which material is received into or issued from a store
under some form of authorization; or an item is retained for reference purposes.
Outline Process Chart:
An outline process chart is a process chart giving an overall
appearance of a process by recording the main operations and sequences in
appropriate Operations & Inspection.
While Preparing the outline process chart we use Symbols of Operation
and Inspection.
A Brief note of the nature of each operation is made beside the symbol.
In an outline process chart, only the principal operations and the
inspections carried out are recorded to ensure effectiveness.
An Operation process chart is a graphic representation of the sequence
of all operations and inspections taking place in a process. It gives a bird’s
eye sight of the overall activities. Entry points of all material, the sequence
of all operations and inspection associated with the process are noted in the
chart.
An Operation Process Chart
Has The following uses:
(1)
Improved plant layout.
(2)
For specifying the basic manufacturing system.
(3)
For determining the sequence of assembly.
(4)
To introduce a manufacturing system to new technical personnel.
Flow Process Chart:
Flow Process charts are graphic representations of the sequences of
operations, transportation, inspections, delays and storages occurring during a
process or a procedure and include information considered for analysis such as,
time required and distance moved. A flow process chart can be prepared in a
similar manner as to prepare the outline process chart. A flow process chart is
a process chart indicating the sequence of the flow of a product by recording
all the events with the help of process chart symbols.
To develop an understanding how a process or work happening and clearly
documenting how a particular job is done, in addition of that mapping a process
in flow chart format helps us where the process can be improved.
There are Three Types of
Flow Process Charts:
1. Material
or Product type or equipment.
2. Man
type.
3. Machine
type or equipment.
Material or Product type
flow process chart:
Records what happens to the material or product, i.e. the changes the
material or product undergoes in location or condition (includes operation and
transportation).
Man Type Flow Process Chart:
Records the activities of the worker or operator, i.e. what a worker or
operator does. To this type of chart usually the storage term is not applicable.
Machine or equipment type
flow process charts:
Records the manner in which a machine or an
equipment is used.
General Guidelines For
Making A Flow Process Chart:
a.
The details must be obtained by direct observation-chart must not be
based on memory.
b.
All the facts must be correctly recorded.
c.
No assumptions should be made.
d.
Make it easy for future reference.
e.
All the charts must have the following details:
1. Name of the product,
material or equipment that is observed.
2. Starting point and ending
point.
3. The location where the
activities take place.
4. The chart reference number,
sheet number, and number of total sheets.
5. Key to the symbols used must
be stated.
Objective of Flow Process
Charts:
1. Set out a sequence of flow
of events occurring in the process.
2. To study the event in a
systematic way.
a. To improve the layout.
b. To improve material
handling.
c. To reduce delays.
d. To eliminate, combine or
rearrange the events in a systematic way.
3. To compare between two or
more alternative methods.
4. To select operations for
detail study.
Two-handed Flow process
chart:
Two-handed flow process chart, is a motion study where the study is
done to analyze the motions used by a worker in performing an activity. The aim of this investigation is to eliminate
or reduce the unwanted motion to a minimum and to arrange the best motions in a
possible sequence. The Two-handed process chart is also known as Left and Right
Hand process chart. In this chart the activities of a worker’s hands are
recorded in their relationship to one another.
A Two-handed process flow chart individually shows the movement of each
hand in a manual process. It is typically used for repetitive operation when
analyzing a manual assembly process, to help make it easier to perform.
General Guidelines For
Preparing the Two-handed process flow chart:
1.
Provide all information about the job in the chart.
2.
Study the operation cycle a few times before starting to record.
3.
Record one hand at a time.
4.
First record the activities of the hand which starts the work first.
5.
Do not combine the different activities like operations, transport etc.
In summary, the two-hand process
chart is an effective tool:
1. Balance the motions of
both hands and reduce fatigue.
2. Reduce or eliminate
nonproductive motions.
3. Shorten the duration of
productive motions.
4. Train new operators in
the ideal method.

No comments:
Post a Comment